- Home
- リソース
- ヒントとコツ
Tips & Tricks
Visual-Environment Highlight of Visual-Seat: STAN Thermal Dummy
STAN is a thermal dummy to test thermal comfort and moisture management characteristics of automobile, truck, and airplane seating. This device is commercialized by Thermetrics® and some relevant information can be found here: https://thermetrics.com/products/manikin/stan/. In collaboration with Thermetrics, ESI developed a numerical model of the STAN dummy for the prediction of its thermal behavior. No humidity is managed in this version of the model. A process for the setup of the seating and the thermal simulations of the STAN dummy have been added in this version.
Christian
Marca
Virtual Seat, Virtual Integration Platform
Visual-Environment Highlight of Visual-Seat: Sewing Simulation Guided Setup
Sewing simulations aim at assembling flat cover patterns and wrapping them around deformable foam block. This application exists in Visual-Seat for many versions as a set of toolboxes and functionalities enabling to set-up this type of input. This has been enhanced with a workflow gathering all tools and functionalities and proposing them in the right sequential order to provide some user guidance.
Christian
Marca
Virtual Seat, Virtual Integration Platform
Visual-Environment Highlight of Visual-Seat: Foam Blocks Positioning
When assembling the different components of the seat, it may happen that the foam at rest is intersecting the frame and/or the suspensions. In order to remove those intersections, a simulation-based technique had been implemented previously by applying surface pressure on foam. Upon customer request, a new method has been added where the frame (and suspensions) can be scaled down and moved initially to retrieve progressively their size and position during simulation, when the contact with foam is active.
Christian
Marca
Virtual Seat, Virtual Integration Platform
Static comfort – Different encrypted data display
How to display encrypted occupant when other data are also encrypted in the model.
Virtual Seat
Static Comfort - Sensors Grid
Sensors Grid Definition improvement in Virtual Seat Solution v2015 (VE 11)
Cécile
Cabane
Virtual Seat
Trim Manufacturing – Trim Adviser
Trim Adviser improvement in Virtual Seat Solution v2015 (VE 11)
Cécile
Cabane
Virtual Seat
How to report and talk about simulation time in an objective manner
Reporting or talking about simulation time is a difficult subject. In the article a way to manage this problem in an objective manner is given.
Harald
Porzner
Welding & Assembly
Materials in the database - Which material properties to use with respect to the three methods to simulate the heat effects of welding
A material is described with exactly one set of material properties. In simulation engineering - depending on the applied method and the moment in time when the simulation is carried out in the product development cycle - only subsets of a full material data set might be required. In this article is outlined which subset is used for which purpose, what is available in the database, and what can be simulated.
Harald
Porzner
Welding & Assembly
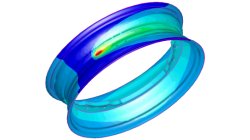
The transient method – the third out of three methods to simulate the heat effects of welding
In order to meet different requirements from first design to start of production, three different methods are available in the Virtual Welding & Assembly Suite from ESI. The third one – the transient method – is used when not only distortion but also residual stresses and microstructure need to be evaluated. The part size allows running a heat source gradually. Compare it with a formability evaluation in sheet metal forming. A motorcycle rim may serve as an example.
Harald
Porzner
Welding & Assembly
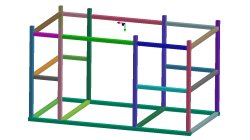
The instantaneous method – the second out of three methods to simulate the heat effects of welding
In order to meet different requirements from first design to start of production, three different methods are available in the Virtual Welding & Assembly Suite from ESI. The second one – the instantaneous method – is used when not only distortion but also residual stresses and micro-structure needs to be evaluated, but welded designs are so huge that it would make no more sense to use a classic transient method with a moving heat source – the simulation time would be too long. Compare it with a feasibility evaluation in sheet metal forming. A frame as produced in machine building, with more than 100 welds, may serve as an example.
Harald
Porzner
Welding & Assembly