VPS Explicit - Basic Crash Modeling
Learn about and understand the basic aspects of crash simulations. Discover how to set up a simple component crash model step by step with all essential options, evaluate the results, and confirm their plausibility.


Audience
Engineers that use VPS/PAM-CRASH to solve dynamic structural problems.

Prerequisites
Basic knowledge of the Finite Element Method is beneficial.
LEARNING PATH
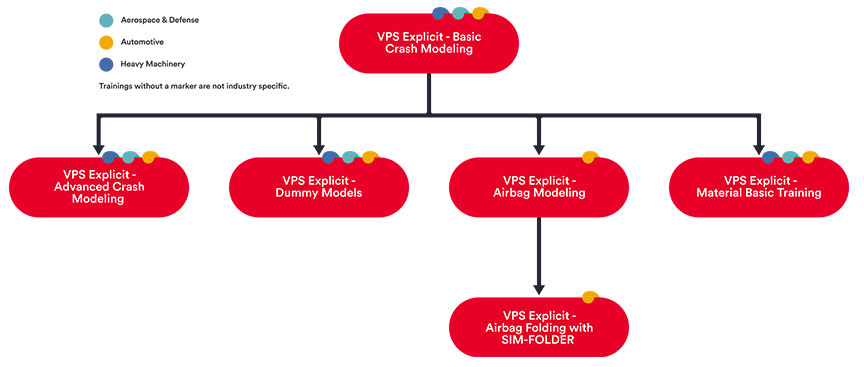

SUGGESTED COURSES

概要
For efficient and successful working with VPS/PAM-CRASH, a solid understanding of the basic algorithms of an explicit code, as well as of the essential program options, are necessary. Therefore, after a short overview of the history of crash simulation and the general capabilities of VPS/PAM-CRASH, the course will give an introduction to how to solve structural problems with explicit time integration. Subsequently, all options will be explained, which are required to perform a standard crash simulation. The course is accompanied by exercises.

TRAINING PROGRAM
Day 1
- Theory of explicit FEM
- Pre-/post-processing, input/output structure
- Boundary conditions, external loads
- Element types
Day 2
- Material models
- Kinematic options
- Contact modeling
- Rigid bodies, spotweld modeling
Day 3
- Modeling elastic-plastic problems
- Time step control
- Restart, Energy balance, stability