- Home
- Resources
- Tips & Tricks
Tips & Tricks
Why it is useful to describe problems in terms of non-dimensional parameters and which ones are the main important in solidification?
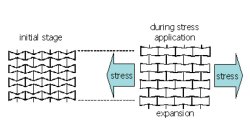
A dimensionless quantity is a quantity without any physical units. Such a number is typically defi ned as a product or ratio of quantities which do have units, in such a way that all units cancel. Dimensionless quantities are widely used in the fields of physics and engineering but also in every day life.
Casting
Influences of Solidification Length and Pressure Intensification on Gas Shrinkage Microporosity in Casting Components
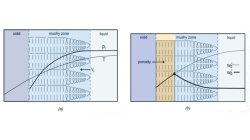
Porosity in castings is a major defect since it affects the mechanical properties. In particular porosities are sites for the initiation of fatigue cracks. Therefore, the reduction of porosity fraction and size, the control of porosity distribution and morphology are crucial for the optimization of mechanical resistance of as cast components.
Casting
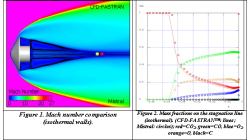
CFD-FASTRAN/CFD-ACE+ coupling for thermal environment simulations
In certain applications, different regions of the computational domain experiences flow conditions that are so different that it is very difficult for a single solver to produce accurate results at the extremes. In many situations, such problems can be separated and solved using loosely coupled solvers. Each solver is chosen to provide highly accurate solutions for the prevailing flow conditions.
Abraham
Meganathan
CFD
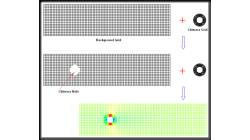
Avoiding Chimera Errors in CFD-FASTRAN
This note discusses a common error encountered by users when trying chimera meshes in CFD-FASTRAN. Such errors are easy to avoid and hopefully this note will assist you.
Abraham
Meganathan
CFD
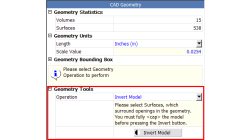
Inverting Models in CFD-CADalyzer
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) requires the discretization of a geometry bounded by it's wetted surfaces. In CAD, the solid parts are created without the corresponding fluid volumes, i.e. negative space.
Abraham
Meganathan
CFD
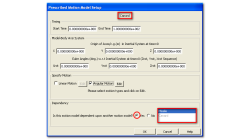
Motion Model Dependencies in CFD-FASTRAN
Moving-body models available in CFD-FASTRAN are highly suited to simulate complex prescribed and six-degree-of-freedom (6DOF) motions of rigid bodies. In many engineering problems, this translates to multiple bodies moving relative to one another.
Abraham
Meganathan
CFD
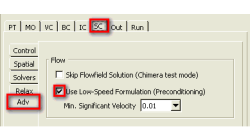
Low Mach Preconditioning and Dual Time Stepping in CFD-FASTRAN
Density-based schemes employing time-marching procedures available in CFD-FASTRAN provide excellent stability and convergence characteristics for high-speed compressible flows (typically M >0.5).
Abraham
Meganathan
CFD
Axisymmetric 2D Convergent-Divergent Boattail Nozzle Simulation Using CFD-FASTRAN
The NASA D-1.22-L boattail nozzle configuration was obtained from the MADIC (Multidisciplinary and Design Industrial Consortium) program. The geometry definition and the flow conditions are documented in NASA TP 1766 [1]. This user tip presents a validation of numerical methods against experimental data.
Abraham
Meganathan
CFD
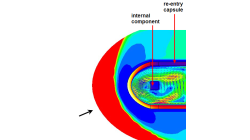
Chemical-kinetic Model for Mars Atmosphere Re-entry Applications
The shock layer flow over a blunt body entering a planetary atmosphere at a hypersonic speed will dissociate and partially ionize. A reliable prediction of the flow-field for such application requires a chemical-kinetic model. For Mars atmosphere, the five species Park'94 is considered [1]. The dissociation of CO2 is producing C, CO, CO2, O and O2.
Abraham
Meganathan
CFD
Improvements to Parallel Simulation Setup in CFD-FASTRAN
Setting up and launching a parallel simulation has become much simpler and easier in FASTRAN. This note discusses some of these developments. Let’s start with things that have not changed. There are still two versions of CFD-FASTRAN solvers for parallel cases. The difference between the two versions is the underlying parallel communication mechanism, the choice of which is decided by the type of mesh used.
Abraham
Meganathan
CFD