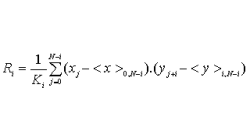- Home
- Resources
- Tips & Tricks
Tips & Tricks
CFD-VIEW: Save Smaller mdl Files
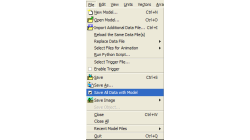
While working with CFD-VIEW, the user has the option of saving an mdl file. This file stores all the entities created in CFD-VIEW, from the point the DTF file (or other data file) was imported, to their current state at the time of saving. The user can thus reopen this file anytime later to resume work.
Abraham
Meganathan
CFD
Plotter Operations with CFD-VIEW
The Plotter operator in CFD-VIEW supports signal processing for Time History data. A previous user tip – Digital Signal Processing using CFD-VIEW – shows how time history date can be made available and how to perform a PSD on a periodic signal. The aim of this new user tip is to list all options supported by the Plotter Operator.
Abraham
Meganathan
CFD
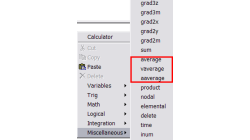
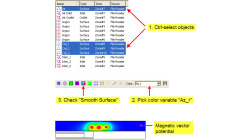
Getting Average Quantities in CFD-VIEW
Many times, post-processing results requires computing average quantities of variables over a surface or volume. CFD-VIEW makes it easy with three calculator functions under the ‘Miscellaneous’ function category, as shown in Figure 1.
Abraham
Meganathan
CFD
Digital Signal Processing using CFD-VIEW
Signals (stream of data) obtained from physical or numerical experiments often require additional processing to understand/interpret the physics they represent. The processing of signals through digital means is termed Digital Signal Processing (DSP).
Abraham
Meganathan
CFD
Plotting Multiple Variables in the CFD-VIEW Plotter
Plotting two or more variables on same plot having values of different magnitude/scale becomes difficult or many times impossible. In these cases plotting data with multiple Y-axes becomes very useful and sometimes necessary.
Abraham
Meganathan
CFD
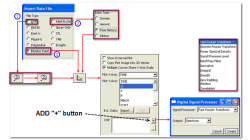
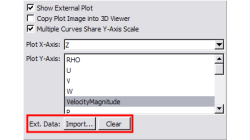
Importing external data in the CFD-VIEW Plotter
Comparing computational results to experimental data is a task often asked of CFD analysts and engineers. The line/curve plotter in CFD-VIEW is commonly used for plotting computational results along curves, such as line probes, surface slices, time histories, etc. CFD-VIEW offers a feature that allows users to import experimental or other external data in the same plot, thus making it easy to compare results.
Abraham
Meganathan
CFD
User Defined Curve Probes in CFD-VIEW
CFD-VIEW allows the user to create curve probes from a file containing XYZ data. This feature gives the user flexibility of collecting data on any specified/desired curve in the computational domain. As an example of use, these "curved line" probes could be used to sample simulation data at the same locations that experimental data was collected.
Abraham
Meganathan
CFD
Tracking Multiple Variables with Multiple Legends
When post-processing with CFD-VIEW, one may wish to display two different variables on two different objects. This requires the use of two legends to correspond to the different color mapping of the variables. The legend tracking feature in CFD-VIEW can be used to achieve this. If this topic is of interest to you, please read on.
Abraham
Meganathan
CFD
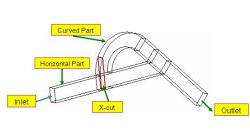
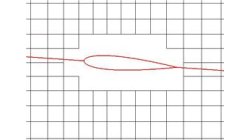
Clipping of X, Y, Z, Arbitrary Cuts and Iso-Surfaces in CFD-VIEW
In CFD-VIEW, performing X, Y, Z, arbitrary cut and iso-surface operations on volumes yield surface objects. One may desire to visualize and/or perform calculations in a user specified spatial range of the surface instead of the whole surface.
Abraham
Meganathan
CFD
Blanking Option in CFD-VIEW for Visualizing Chimera Grids
CFD-FASTRAN uses closed surfaces, such as walls or blocked regions, to create Chimera holes (or blanked regions) in a grid. By default, the number of buffer layers is set to 1. This means that a closed surface will cut a hole in any mesh that overlaps it, and the initial "blanking" of grid cells defines the hole.
Abraham
Meganathan
CFD