- Home
- Resources
- Tips & Tricks
Tips & Tricks
e-café #3- Modélisation des opérations de poteyage et soufflage à l’aide Quik CAST™
Modélisation des opérations de poteyage et soufflage à l’aide Quik CAST™
Mathieu
Moerckel
Casting
e-café #2- Prédiction de la localisation des inclusions de sable à l’aide de ProCAST™
Prédiction de la localisation des inclusions de sable à l’aide de ProCAST™
Mathieu
Moerckel
Casting
e-café #1- Détermination de la courbe de déplacement du piston à l’aide de ProCAST™
Détermination de la courbe de déplacement du piston à l’aide de ProCAST™
Mathieu
Moerckel
Casting
Process optimization: the future of numerical simulation software
Optimization is becoming a very popular word. However, what does it mean and what does it involve? The goal of this e-tip is to give some keys about optimization concepts and its use in process optimization. In a first stage, we will describe the type of optimization problems that could be solved and in a second stage, the principles and algorithms will be presented. Finally, advantages and drawbacks of the different methods and algorithms will be addressed, with respect to the different types of optimization problems which can be solved.
Casting
Casting simulation: from prototype to performance
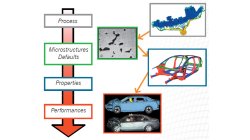
Passenger safety in cars, planes and other transportation vehicles is an ethical obligation, a legal issue and a technological challenge. Simulation is a well implemented tool in order to test the behaviour of a car body during crash. The models, including rapid deformation and rupture, are sophisticated and reliable. Currently, most properties used in such simulations correspond to homogenous and defect free materials. However, cars are manufactured before being crashed. And manufacturing routes such as casting, but also stamping, forging or welding, do not provide defect free and homogeneous materials.
Casting
Parallel processing
“To pull a bigger wagon, it is easier to add more horses than to grow a gigantic horse.” This paraphrased quotation nicely expresses the basic concept of parallel processing. The speed of sequential computers has been doubling every eighteen months, according to Moore’s law. However, at any given time, that speed is limited by the state of the art in integrated circuit design and manufacturing. To circumvent that limitation, it is possible to split a given computationally intensive task among multiple processors working simultaneously.
Bohus
Ulrych
Casting
The manufacturing of sand cores
The manufacturing of iron, steel and non-ferrous castings is achieved using a variety of casting process designs, and most of these involve the use of sand cores which form the internal shape of the casting. A good quality casting requires a good quality core. Dimensional stability, uniform density, strength, hardness and permeability are some of the characteristics that need to be controlled. A good core must have suffi cient strength and hardness to be handled and to resist during the pouring of liquid metal. Suffi cient permeability is also necessary for the escape of gases generated during the casting process. The diff erent manufacturing processes and some of the issues related to core production will be discussed here.
Casting
Critical issues in modelling investment casting
Reduce part development lead-times by a better knowledge of process and an early confi rmation of metallurgical capabilities is one of the main topics for investment casting technology. Numerical simulation is one of the major tools which can be used to face this goal. This e-tip illustrates a simulation methodology usable to optimize a casting design in an effi cient and rapid way.
Casting
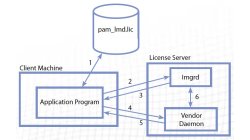
FLEXlm protection file system
ESI group needs to license, manage and track a variety of licensing options, platform and product dependencies. FLEXlm is one of the only software that is up to this task. A simple, shrinkwrapped license management product would not be powerful and flexible enough to license all ESI products.
Casting
The challenge of simulating casting and heat treatment
Foundries that have implemented casting simulation to shorten development time, further wish to use simulation in order to reduce the cost of subsequent processing steps. This often requires the simulation of heat treatment.
Casting, Welding & Assembly