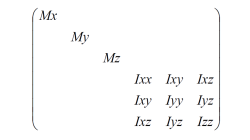- Home
- Resources
- Tips & Tricks
Tips & Tricks
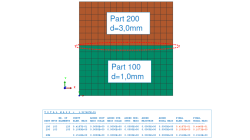
Why do total mass, sum of part masses and sum of nodal masses not match ?
This tip discusses the possible discrepancies in informations concerning total mass, part masses, nodal and element masses, given in the Virtual Performance Solution (VPS) output listing.
Jürgen
Rueckert
Virtual Performance
Which moments of inertia to use in added mass (MASS / ) cards ?
This tip discusses the choice of physically meaningful numbers to be used, when moments of inertia need to be specified in an added mass definition.
Jürgen
Rueckert
Virtual Performance
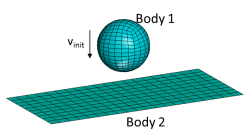
Some possible problems with CNTAC or TIED definitions
This tip discusses some of the reasons that might be responsible for problems with contact or tied definitions in a VPS simulation
Jürgen
Rueckert
Virtual Performance
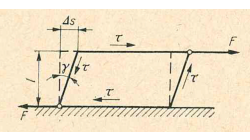
Relation between Bulk Modulus K, Shear Modulus G, Young's Modulus E and Poisson's ratio ν
This tip explains the relations between the parameters that describe the linear elastic behavior of materials
Jürgen
Rueckert
Virtual Performance
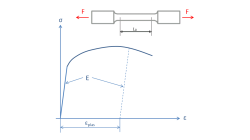
How to convert force-deflection into true stress-strain curves?
This tip helps to convert typical tensile test data into stress-strain curves to be used in many material models of Virtual Performance Solution (VPS)
Jürgen
Rueckert
Virtual Performance
Weld Fatigue analysis based on the Dang Van Criteria
Numerical modeling of fatigue behavior has become critical for welding applications. For this purpose the ‘Dang Van criterion’ has been integrated in SYSWELD for fatigue evaluation of welded structure under multi-axial loadings. The Dang Van fatigue damage criterion is used to predict crack initiation and life duration of components subjected to damaging load. This criterion is based on multi-scale approach which assumes that shakedown occurs before crack initiation.
Harald
Porzner
Welding & Assembly
How to report and talk about simulation time in an objective manner
Reporting or talking about simulation time is a difficult subject. In the article a way to manage this problem in an objective manner is given.
Harald
Porzner
Welding & Assembly
Materials in the database - Which material properties to use with respect to the three methods to simulate the heat effects of welding
A material is described with exactly one set of material properties. In simulation engineering - depending on the applied method and the moment in time when the simulation is carried out in the product development cycle - only subsets of a full material data set might be required. In this article is outlined which subset is used for which purpose, what is available in the database, and what can be simulated.
Harald
Porzner
Welding & Assembly
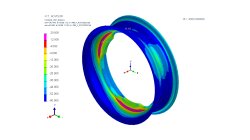
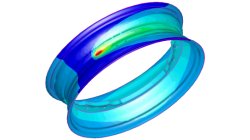
The transient method – the third out of three methods to simulate the heat effects of welding
In order to meet different requirements from first design to start of production, three different methods are available in the Virtual Welding & Assembly Suite from ESI. The third one – the transient method – is used when not only distortion but also residual stresses and microstructure need to be evaluated. The part size allows running a heat source gradually. Compare it with a formability evaluation in sheet metal forming. A motorcycle rim may serve as an example.
Harald
Porzner
Welding & Assembly
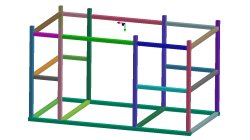
The instantaneous method – the second out of three methods to simulate the heat effects of welding
In order to meet different requirements from first design to start of production, three different methods are available in the Virtual Welding & Assembly Suite from ESI. The second one – the instantaneous method – is used when not only distortion but also residual stresses and micro-structure needs to be evaluated, but welded designs are so huge that it would make no more sense to use a classic transient method with a moving heat source – the simulation time would be too long. Compare it with a feasibility evaluation in sheet metal forming. A frame as produced in machine building, with more than 100 welds, may serve as an example.
Harald
Porzner
Welding & Assembly